Understanding the intricacies that distinguish a bipolar brain from a typical brain is vital in unveiling the enigma surrounding bipolar disorder. This exploration offers a deep dive into the neurological impact of bipolar disorder, shedding light on the often-misunderstood phenomenon of bipolar brain fog. Furthermore, it seeks to unravel the question of whether a specific brain type is intrinsically linked to bipolar disorder, fostering a more comprehensive understanding of this complex mental health condition. Through scientific insights and emerging research, this article aims to provide clarity and enhance awareness of the neurological facets of bipolar disorder.
Structural And Functional Brain Differences
Studies utilizing neuroimaging techniques have revealed distinct structural and functional abnormalities in the brains of individuals with bipolar disorder. Structurally, variations in the size and integrity of the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making and impulse control, have been observed. These changes may contribute to the impaired judgment and erratic behavior often seen during manic episodes. Additionally, the limbic system, which includes areas like the amygdala and hippocampus, is crucial in regulating emotions and memory. In individuals with bipolar disorder, these regions may show hyperactivity or hypoactivity, correlating with emotional instability and cognitive deficits. Functional connectivity between these regions and others, such as the anterior cingulate cortex, is also disrupted, leading to impaired emotional regulation. These findings not only deepen our understanding of the neural underpinnings of bipolar disorder but also underscore the potential for targeted interventions that address these specific neural dysfunctions..
The Role Of Neurotransmitters
In exploring the intricate mechanisms of mental health, it's crucial to consider the profound impact that neurotransmitters have on both the bipolar and the normal brain. In individuals with bipolar disorder, the delicate equilibrium of neurotransmitters—such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine—is often disturbed, leading to pronounced fluctuations between manic and depressive episodes. These chemical imbalances not only influence mood but also affect cognitive functions, energy levels, and overall emotional regulation. Conversely, the normal brain operates with a more consistent neurotransmitter balance, enabling a steadier emotional state and more predictable responses to environmental stimuli. Understanding these differences highlights the complex biological underpinnings of bipolar disorder and underscores the importance of targeting neurotransmitter regulation in therapeutic interventions..
Understanding Bipolar Brain Fog

Bipolar brain fog, a lesser-known yet impactful symptom of bipolar disorder, can considerably alter an individual's ability to function effectively in daily situations. This cognitive dysfunction often leads to noticeable lapses in concentration, making it challenging to focus on tasks for extended periods. Additionally, memory issues may become evident, ranging from simple forgetfulness to more severe disruptions in recalling recent events or information. Decision-making is another area heavily affected, where individuals may experience indecisiveness or find themselves overwhelmed by choices they could previously manage with ease. These cognitive impairments underscore the contrasts between a bipolar and a neurotypical brain, illustrating how deeply mood disorders can affect one's mental processes. Addressing these challenges requires awareness and tailored strategies to help individuals navigate daily life with more ease and confidence..
Imaging Insights Into Bipolar Brains
Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, have provided deeper insights into the differences between bipolar brains and normal brains. These scans have revealed variations in the size and activity levels of certain brain regions. For instance, the amygdala—responsible for emotion processing—often shows increased activity during manic episodes. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, which plays a crucial role in decision-making and impulse control, can exhibit altered functioning, potentially contributing to the impulsivity often observed in individuals with bipolar disorder. Furthermore, changes in the hippocampus, a region associated with memory and recognition, may help explain cognitive challenges faced by sufferers during different phases. These imaging findings not only deepen our understanding of the neurobiological underpinnings of bipolar disorder but also pave the way for more targeted therapeutic approaches, potentially leading to improved management and outcomes for those affected by the condition. Through ongoing research and technological advancements, we continue to unravel the complex interplay of brain structures and functions that characterize mental health disorders..
Brain Type Theories: Is Brain Type 8 Bipolar?

The intricacies of the human brain have long fascinated scientists, and the quest to understand the links between brain types and mental health disorders remains a priority. In the debate over whether "brain type 8" might predispose individuals to bipolar disorder, researchers are focusing on how variations in brain structure and function might influence mental health outcomes. Advanced imaging techniques and genetic studies are being employed to uncover subtle neural patterns and genetic markers associated with bipolar disorder, attempting to map these back to specific brain types. Although conclusive evidence is elusive, the potential discovery of such associations could revolutionize diagnostic and treatment approaches, enabling more personalized interventions. As scientists continue their investigations, there is a cautious optimism that these endeavors might one day clarify the biological underpinnings of bipolar disorder and improve the predictability of its onset in individuals with particular brain characteristics..
Biochemical Factors In Bipolar Disorder
In addition to hormonal imbalances and HPA axis dysregulation, neurotransmitter systems also play a crucial role in the biochemical landscape of the bipolar brain. Alterations in the levels and functioning of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine are often observed, which can lead to the characteristic mood swings and emotional dysregulation inherent in bipolar disorder. Furthermore, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress are gaining attention as significant biochemical factors that may exacerbate neural damage and synaptic dysfunction. These biochemical disturbances not only underscore the complexity of bipolar disorder but also highlight potential targets for therapeutic intervention, aiming to restore biochemical equilibrium and improve clinical outcomes. As research progresses, there is hope that a deeper understanding of these biochemical pathways will lead to more effective treatments and improved quality of life for those affected by bipolar disorder..
Treating The Bipolar Brain
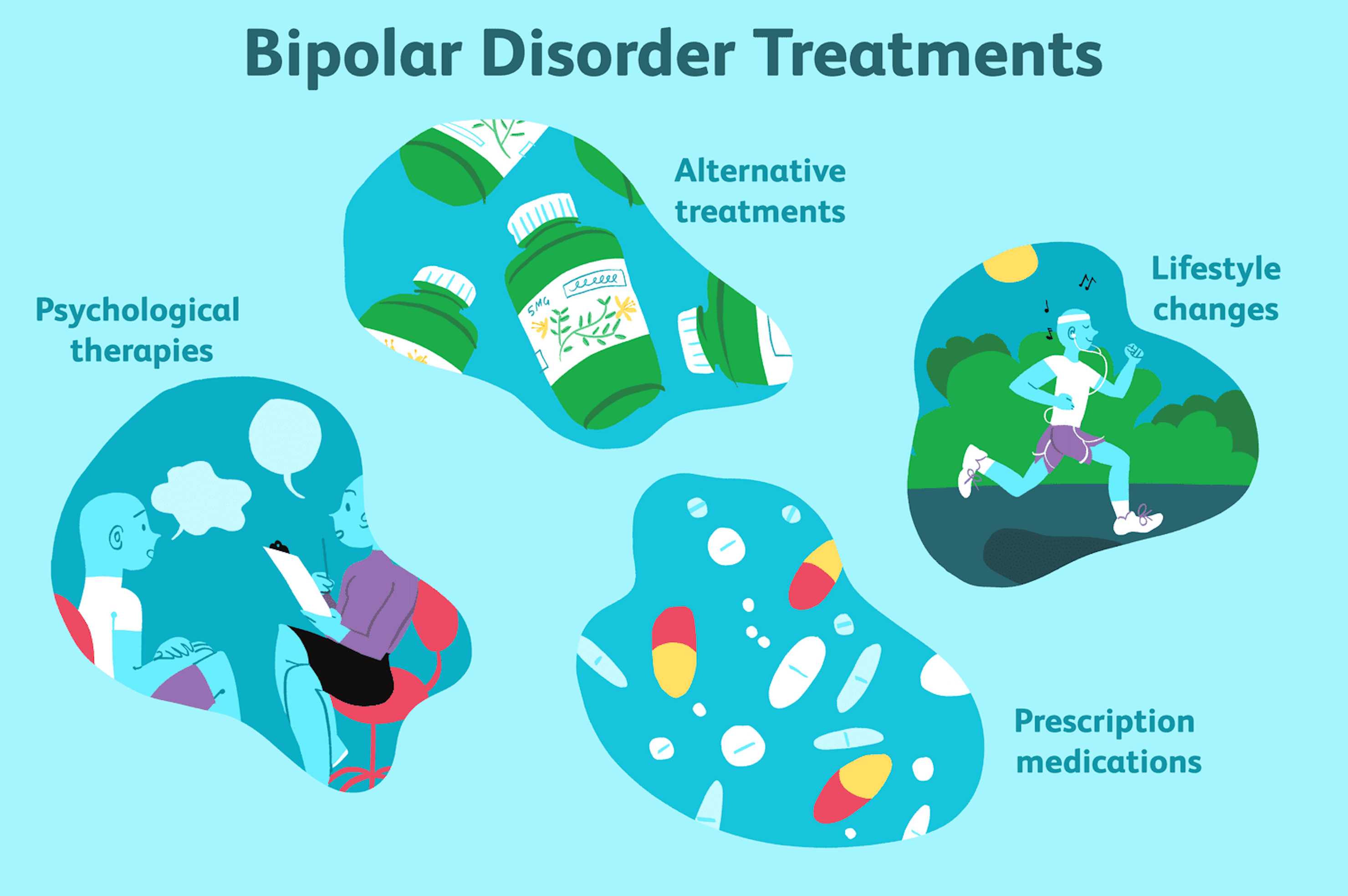
Medications used to manage bipolar disorder, such as mood stabilizers and antipsychotics, aim to target and rectify the neurological disparities present in affected individuals. These medications function primarily by adjusting neurotransmitter levels, notably those of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, which are often dysregulated in bipolar disorder. Furthermore, they help in calming hyperactive brain regions, such as the amygdala, which is linked to emotion regulation and is frequently overactive during manic episodes. Through these mechanisms, treatments endeavor to harmonize brain activity, facilitating a state that more closely mirrors typical cognitive functioning. Nonetheless, it is important to recognize that the efficacy and side effects of these medications can vary significantly among individuals, necessitating personalized treatment plans and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals to achieve optimal outcomes. Additionally, ongoing research continues to explore novel therapies and combinations to enhance the effectiveness and tolerability of treatments for bipolar disorder, aiming to improve quality of life for those affected..
Therapeutic Strategies

In addition to therapy, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, engaging in regular physical activity, and adhering to a healthy diet can significantly contribute to managing bipolar disorder. These routines provide stability and support mental health, complementing the effects of therapy. Mindfulness practices and stress-reduction techniques, like meditation and yoga, also play a vital role in maintaining emotional balance. Support from family and friends creates a network of understanding that can ease the journey by providing encouragement and reducing feelings of isolation. By integrating these lifestyle changes with therapies such as CBT and interpersonal therapy, individuals can achieve a more harmonious state of well-being, fostering resilience against mood fluctuations and enhancing everyday functioning..
In summary, the insights gained from distinguishing between the bipolar brain and a typical brain are invaluable in enhancing our approaches to managing and treating this complex disorder. As research progresses, uncovering the precise mechanisms by which bipolar disorder influences brain function will facilitate the development of innovative and targeted therapies. Such advancements not only promise to improve clinical outcomes but also empower individuals with bipolar disorder to lead lives marked by stability and well-being, reducing stigma and fostering greater acceptance and awareness in society.