Recognizing and differentiating between mental health disorders is essential for ensuring accurate diagnoses and effective treatment strategies. Among the most frequently misunderstood are Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder, which often blur in public perception due to their overlapping symptoms. Despite both disorders affecting mood regulation and interpersonal dynamics significantly, they each possess unique attributes that define their causes, manifestations, and therapeutic approaches. Disentangling these complexities not only aids in better clinical outcomes but also fosters a deeper empathy and understanding for those navigating these mental health challenges.
The Distinguishing Characteristics Of Bipolar Disorder Versus Borderline Personality Disorder
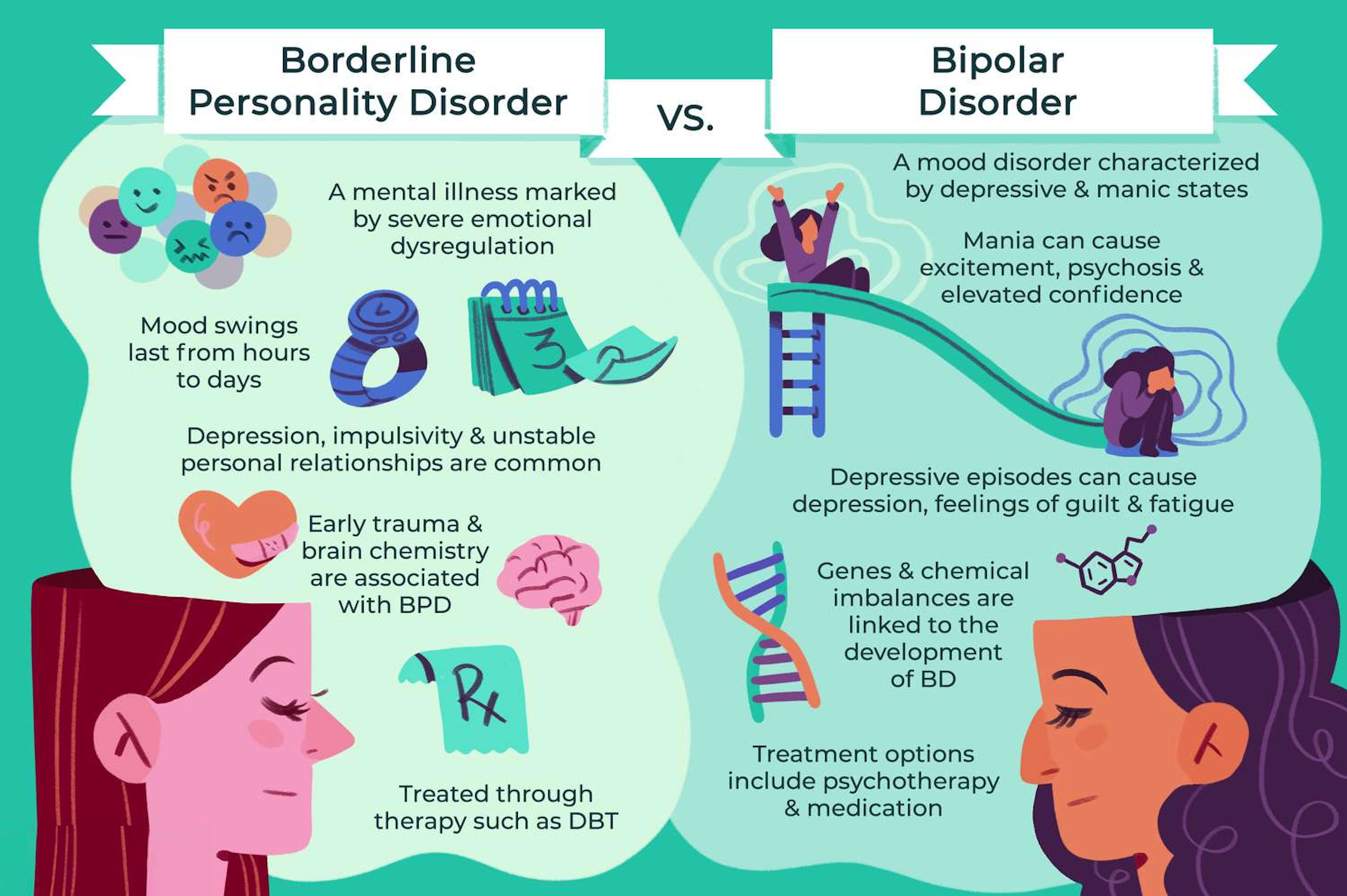
Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder, though often confused due to overlapping symptoms such as mood instability, fundamentally differ in their underlying mechanisms and manifestations. Bipolar Disorder is marked by pronounced episodes of mania or hypomania and depression, where an individual may experience heightened energy levels, euphoria, or irritability, followed by periods of deep sadness, hopelessness, or fatigue. These mood shifts are often cyclical and can last for days, weeks, or even longer, heavily impacting one's ability to function daily. On the other hand, Borderline Personality Disorder is predominantly centered around persistent patterns of turbulent emotions and unstable relationships. Individuals with BPD may grapple with intense feelings of abandonment and a fluctuating self-image, leading to impulsive behaviors and efforts to avoid perceived rejection. They might experience rapid mood swings but these are often triggered by external stimuli, particularly interpersonal interactions, rather than occurring in the prolonged episodes seen in Bipolar Disorder. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for implementing effective therapeutic interventions and support strategies for those affected by these conditions..
Bipolar Disorder Versus Borderline Personality Disorder

Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) are both mental health conditions that involve mood dysregulation, yet they manifest quite differently. In Bipolar Disorder, individuals experience distinct mood episodes, where elevated moods (mania or hypomania) alternate with depressive episodes, often lasting several days or weeks. During manic episodes, individuals may feel euphoric, have increased energy and activity levels, and engage in risky behaviors, whereas depressive episodes can bring profound sadness, lethargy, and hopelessness. In contrast, those with Borderline Personality Disorder endure rapid mood swings that can fluctuate significantly within a single day, often triggered by external events or interpersonal interactions. These mood swings are accompanied by chronic feelings of emptiness, an intense fear of abandonment, and a persistently unstable self-image. Individuals with BPD may also exhibit impulsive behaviors and have tumultuous relationships due to their heightened sensitivity to perceived rejection or criticism. Understanding these differences is crucial for providing appropriate treatment and support for those affected by these complex disorders..
Causes Of Bipolar Disorder Versus Borderline Personality Disorder

Additionally, it is crucial to consider the brain chemistry and hormonal influences that contribute to these disorders. In Bipolar Disorder, neurotransmitter imbalances, such as those involving serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, play a significant role in the mood swings experienced by individuals. These biochemical factors can be exacerbated by lifestyle elements like irregular sleep patterns or substance abuse. In contrast, Borderline Personality Disorder is closely associated with dysfunction in areas of the brain that regulate emotions and impulse control, including the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. This dysfunction may result from both genetic vulnerabilities and environmental stressors, underscoring the importance of early intervention and support. Understanding the distinct pathways leading to each disorder highlights the complexity and need for tailored therapeutic approaches to effectively manage and support affected individuals..
What is the Difference In Treatment Between Each Disorder?

Approaching treatment for these conditions involves tailoring strategies to the unique needs of each disorder. For Bipolar Disorder, a combination of mood stabilizers like lithium, anticonvulsants, and antipsychotic medications often forms the cornerstone of treatment, aimed at alleviating mood swings and preventing the recurrence of manic or depressive episodes. Psychoeducation and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) also play supportive roles, helping individuals manage symptoms and adhere to treatment plans. On the other hand, Borderline Personality Disorder primarily relies on specialized psychotherapy methods. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is particularly effective, as it emphasizes skills such as emotional regulation, distress tolerance, and interpersonal effectiveness, assisting individuals in navigating the intense emotions characteristic of the disorder. While medications might be employed to target co-occurring conditions or specific symptoms like anxiety or depression, they are not the central focus of treatment for BPD. Both disorders require comprehensive and individualized approaches to effectively support those affected..
Impact On Interpersonal Relationships: BPD vs Bipolar

Both disorders significantly impact interpersonal relationships, but in different ways. People with Bipolar Disorder may experience strained relationships due to unpredictable mood swings. These fluctuations, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows, can be bewildering for both the individuals and their loved ones. Partners and family members might struggle to understand the sudden shifts in behavior and emotion, which can lead to confusion and frustration. In contrast, individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder often face challenges such as intense fear of abandonment, idealization, and devaluation of others, leading to turbulent relationships. This deep-seated fear may manifest as clinginess or, conversely, sudden withdrawal when they perceive any sign of rejection, real or imagined. Their relationships often oscillate between extremes, from adoration to disdain, which can leave partners feeling emotionally exhausted. Understanding and empathy from both parties, along with suitable therapeutic interventions, are crucial for fostering healthier, more stable interactions in both scenarios..
The Diagnosis Differences

When diagnosing these conditions, mental health professionals use different criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Bipolar Disorder diagnosis focuses on identifying the presence of manic, hypomanic, and depressive episodes. In contrast, Borderline Personality Disorder diagnosis revolves around identifying pervasive patterns of instability in relationships, self-image, and emotions. Each psychiatric condition requires a nuanced understanding of symptoms and their impact on an individual's daily functioning. In the case of Bipolar Disorder, clinicians look for fluctuating mood states that might include euphoria, increased energy levels, and grandiosity during manic phases, as well as profound sadness, hopelessness, and fatigue during depressive episodes. On the other hand, diagnosing Borderline Personality Disorder entails recognizing chronic feelings of emptiness, intense fear of abandonment, and impulsive actions that can often lead to strained personal connections. Despite some overlapping symptoms, the distinct nature of these disorders necessitates tailored assessment techniques and intervention strategies to effectively address the unique challenges faced by individuals..
Exploring Impulsiveness Between The Two

Both Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder exhibit impulsive behaviors, yet the underlying mechanisms and manifestations of this impulsivity diverge significantly between the two conditions. In Bipolar Disorder, impulsivity often surges during manic or hypomanic episodes, characterized by heightened energy levels, grandiosity, and a decreased need for sleep. These episodes can lead to behaviors such as excessive spending, risky sexual encounters, or other dangerous activities spurred by a euphoric state or an overestimation of one's capabilities. On the other hand, Borderline Personality Disorder is marked by a pervasive pattern of impulsivity that threads through daily life. This chronic impulsivity often serves as a coping mechanism to manage intense emotional distress. It might manifest as binge eating, substance abuse, or self-harming behaviors, all of which are attempts to self-soothe or exert control amidst emotional chaos. Understanding the distinct nature of impulsive behavior in these disorders is crucial for tailoring effective therapeutic interventions that address the specific needs and triggers of each condition..
Misdiagnosis Risks

Misdiagnosis between these two disorders is common due to symptom overlap, leading to improper treatments and prolonged patient distress. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, as it ensures that sufferers receive tailored interventions that target their specific needs. A thorough evaluation by a mental health professional that considers the patient's history, behavior patterns, and symptom onset is essential for differentiating between the two disorders. This comprehensive assessment involves a detailed exploration of the individual's past medical records, psychological evaluations, and even input from close family members or friends. By doing so, clinicians can identify subtle differences and nuances in symptoms that might otherwise be overlooked. Moreover, using validated diagnostic tools and criteria can further support the differentiation process, minimizing the risk of misdiagnosis and ensuring that patients embark on the most appropriate therapeutic path..
Management And Awareness
Effective management of both disorders necessitates understanding the fundamental differences and similarities between them. People affected by these conditions benefit greatly from tailored treatment plans, ongoing support, and increasing mental health awareness. By recognizing the unique symptoms and triggers associated with each disorder, healthcare professionals can develop comprehensive strategies that address the specific needs of individuals. Collaborative care that incorporates medical intervention, therapy, and peer support can significantly enhance outcomes for patients. Additionally, enhancing mental health awareness within communities breaks down stigma and encourages more people to seek help. This collective effort not only improves the quality of life for those directly impacted but also fosters a more inclusive and understanding society. Hence, education and advocacy play pivotal roles in ensuring that affected individuals receive the empathy and care they deserve..
In conclusion, recognizing the nuanced distinctions between Bipolar Disorder and Borderline Personality Disorder is crucial in fostering a more empathetic and informed approach to mental health care. By prioritizing accurate diagnosis and tailoring treatment to the individual needs of those affected, we can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. Raising awareness and promoting education around these disorders not only aids in reducing stigma but also empowers individuals, families, and communities to support one another more effectively. Ultimately, a deeper understanding and acknowledgment of the complexities inherent in these mental health conditions pave the way for a more compassionate and comprehensive mental health support system.


