In the realm of trauma-related mental health issues, the interplay between Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and dissociation presents a formidable challenge to both diagnosis and treatment. This intricate connection demands a nuanced understanding to effectively address and manage these intertwined conditions. By exploring the complex relationship between PTSD and dissociation, this article aims to shed light on the dissociative subtype of PTSD, the unique aspects of complex PTSD (C-PTSD) dissociation, and the distinct manifestations of C-PTSD and dissociation. Through examining these nuanced dimensions, we can better appreciate the complexity of trauma responses and improve the therapeutic approaches for individuals grappling with these profound psychological struggles.
What Is PTSD And Dissociation?

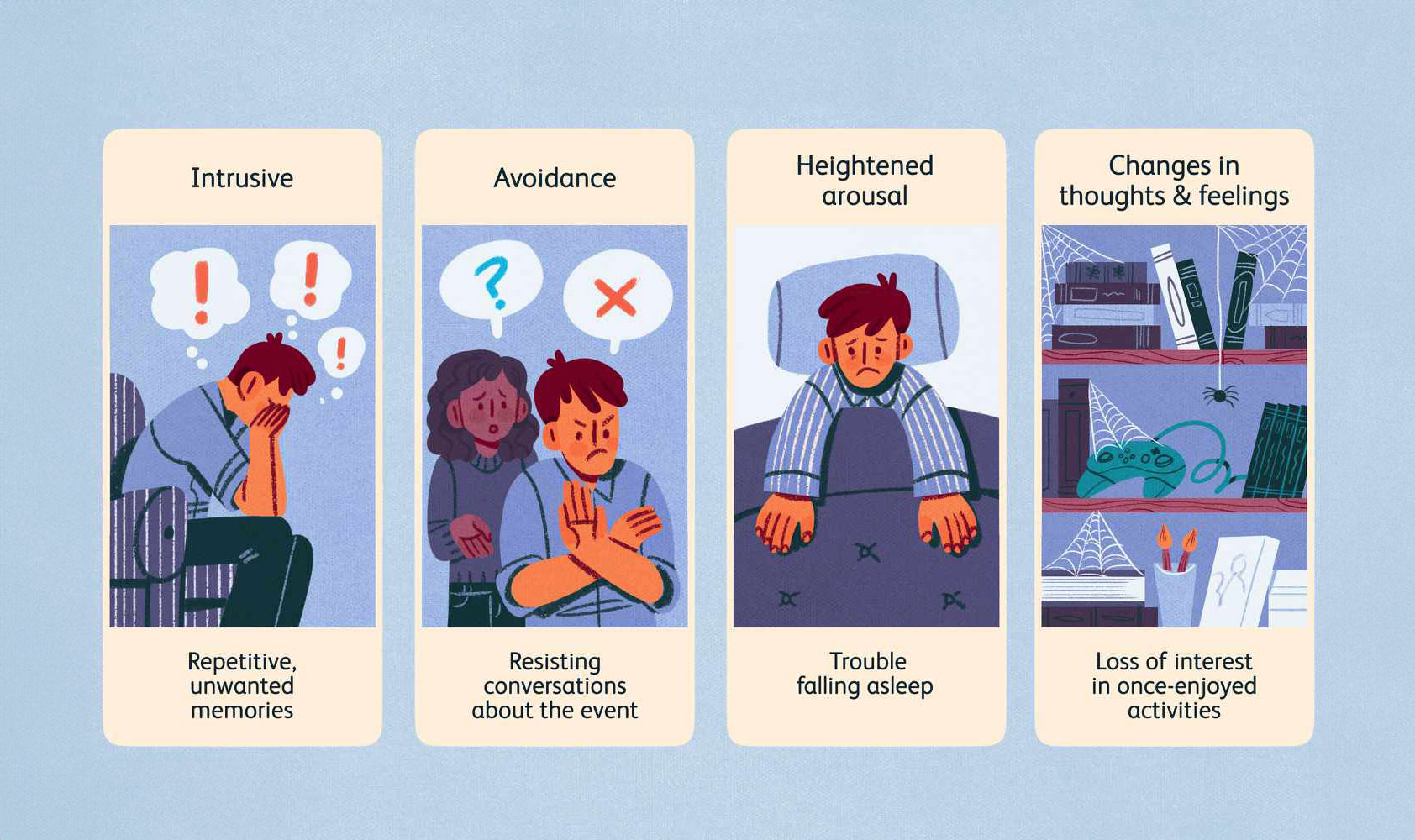
PTSD and dissociation frequently coexist as a response to overwhelming trauma, creating a complex interplay that can complicate the healing process. Individuals suffering from PTSD may find themselves habitually reliving the traumatic event through intrusive memories or vivid flashbacks, often triggering a fight-or-flight response. Dissociation can manifest in these moments as a kind of psychological escape, where the mind distances itself from the emotional turmoil by fragmenting elements of identity and perception. This disconnection might appear as feelings of detachment from reality, a sense of observing oneself from outside the body, or lapses in memory related to the traumatic event. While dissociation can offer short-term relief from the relentless assault of distressing memories and emotions associated with PTSD, over time, it can hinder emotional processing and integration, potentially exacerbating feelings of isolation and confusion. Addressing this duality through therapeutic approaches, like trauma-focused therapy or EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing), can help individuals gradually reconnect with their experiences in a controlled and safe manner, fostering healing and resilience..
Dissociative Subtype Of PTSD
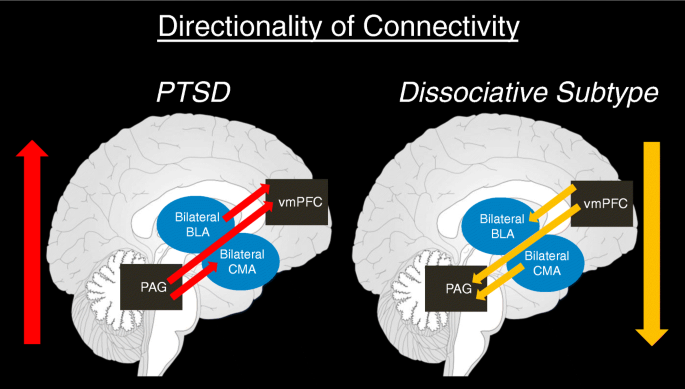
In treating the dissociative subtype of PTSD, it's important for mental health professionals to incorporate therapeutic approaches that directly address the unique experiences of depersonalization and derealization. These symptoms may serve as coping mechanisms, shielding individuals from intense emotions or memories associated with their trauma. Techniques such as grounding exercises, mindfulness, and body awareness practices can help individuals reconnect with their sense of self and reality. Trauma-informed therapies that emphasize creating a safe environment and building a strong therapeutic alliance are also vital. Furthermore, personalized interventions might include cognitive processing therapy and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), adapted to suit the specific needs of those with dissociative symptoms. Understanding the nuanced presentation of the dissociative subtype allows for more effective, compassionate, and holistic treatment plans that empower individuals on their path to recovery..
Understanding Complex PTSD And Dissociation

Complex PTSD, or C-PTSD, often stems from sustained exposure to traumatic experiences, particularly in contexts involving close personal relationships, where an individual feels trapped or powerless. Unlike PTSD, which might arise from a single traumatic event, C-PTSD is the result of recurrent trauma that can significantly disrupt a person's sense of self and identity. One of the most intricate aspects of Complex PTSD is dissociation, where individuals may experience a profound disconnection between their thoughts, memories, and sense of identity. This dissociative state can manifest in feeling detached from oneself or one's emotions, as though living in a constant state of self-alienation. Consequently, individuals with C-PTSD frequently struggle with forming and maintaining healthy relationships, as their ability to trust and connect with others may be severely impaired. Moreover, the pervasive sense of a fragmented self can contribute to a persistent negative self-image and self-criticism, making it difficult to engage in positive self-affirmation. Emotional regulation often becomes a challenge, as individuals might experience intense emotional swings, difficulty managing stress, and episodes of overwhelming depression or anxiety. Addressing these issues requires a nuanced therapeutic approach that emphasizes safety, self-compassion, and gradual reintegration of fragmented aspects of the self..
C-PTSD And Dissociation Symptoms
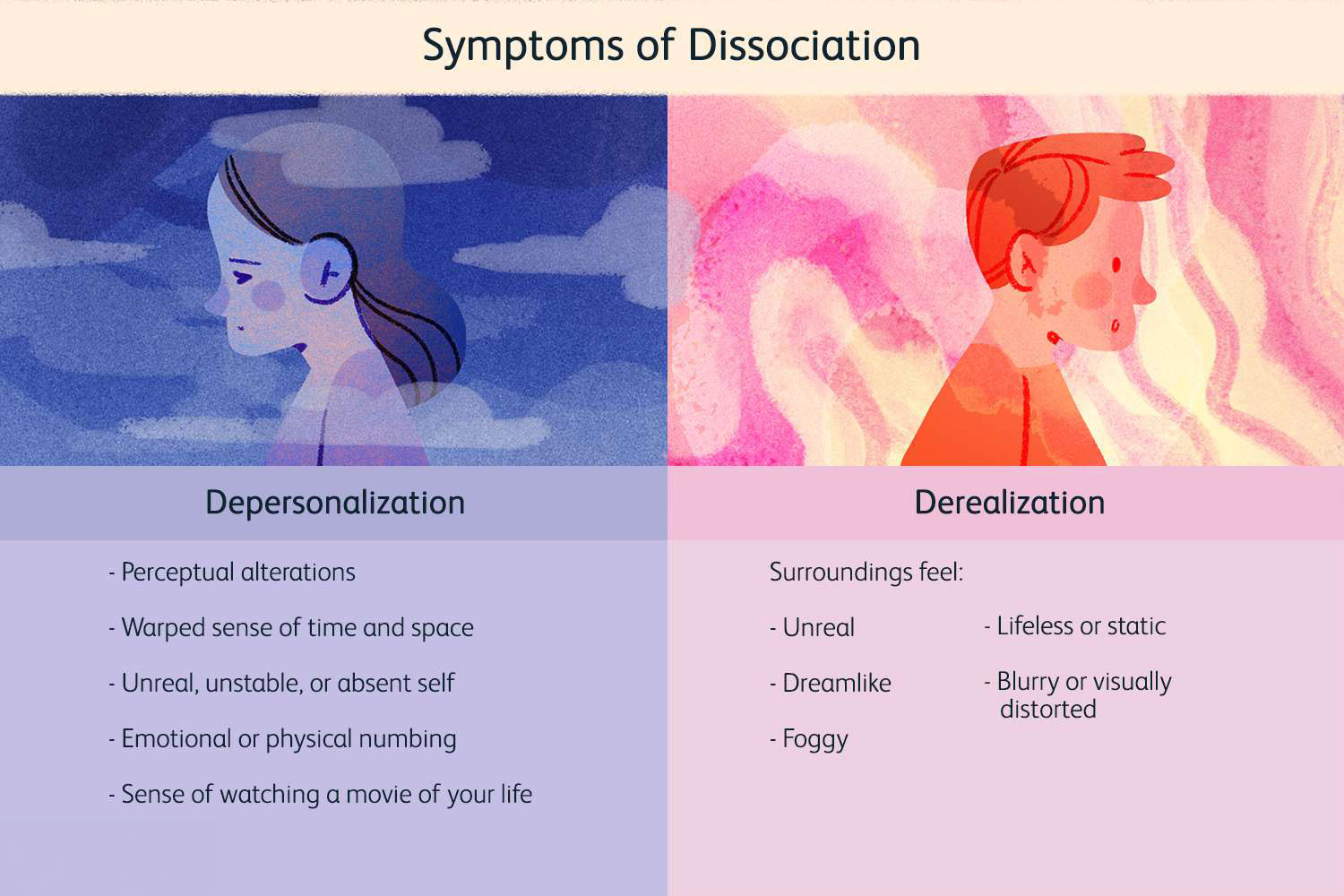
Individuals experiencing C-PTSD and dissociation may find themselves struggling with a pervasive sense of disconnection from their daily lives. This disconnection can manifest as bouts of emotional numbness, wherein individuals are unable to fully experience or express their feelings, leading to challenges in forming and maintaining personal relationships. Alongside this, intrusive memories or flashbacks can abruptly invade their consciousness, often triggered by seemingly innocuous stimuli, and recreate the emotional intensity of past traumas. This can contribute to an unstable sense of self-identity, where individuals feel fragmented, unsure of who they truly are, and oscillate between different personas. Recognizing and acknowledging these intertwined symptoms is crucial, as it opens the door to tailored therapeutic approaches that can help individuals rebuild a coherent sense of self and develop coping strategies to manage their daily experiences. Seeking professional support not only provides validation and understanding but also assists in navigating the complex landscape of trauma recovery..
The Impact Of Dissociation In PTSD

Dissociation in PTSD significantly disrupts an individual's ability to function in everyday settings. This state of disconnection from reality can manifest in the workplace, where concentrating on tasks becomes a formidable challenge, leading to decreased productivity and job security concerns. In personal relationships, dissociation often hinders emotional connection, creating a sense of distance between loved ones that can strain or fracture bonds. Even during moments meant for relaxation, those affected may find themselves detached, unable to engage with activities that once brought joy or solace. This persistent struggle with the present moment contributes to a looming vulnerability to other mental health complications, such as anxiety, depression, and substance abuse disorders, as individuals turn to maladaptive coping mechanisms. Therefore, addressing dissociative symptoms through therapeutic interventions and support systems is vital, as it not only aids in reconnecting with daily life’s realities but also fosters resilience and enhances the overall quality of life for those impacted by PTSD..
Treatment Approaches For PTSD And Dissociation
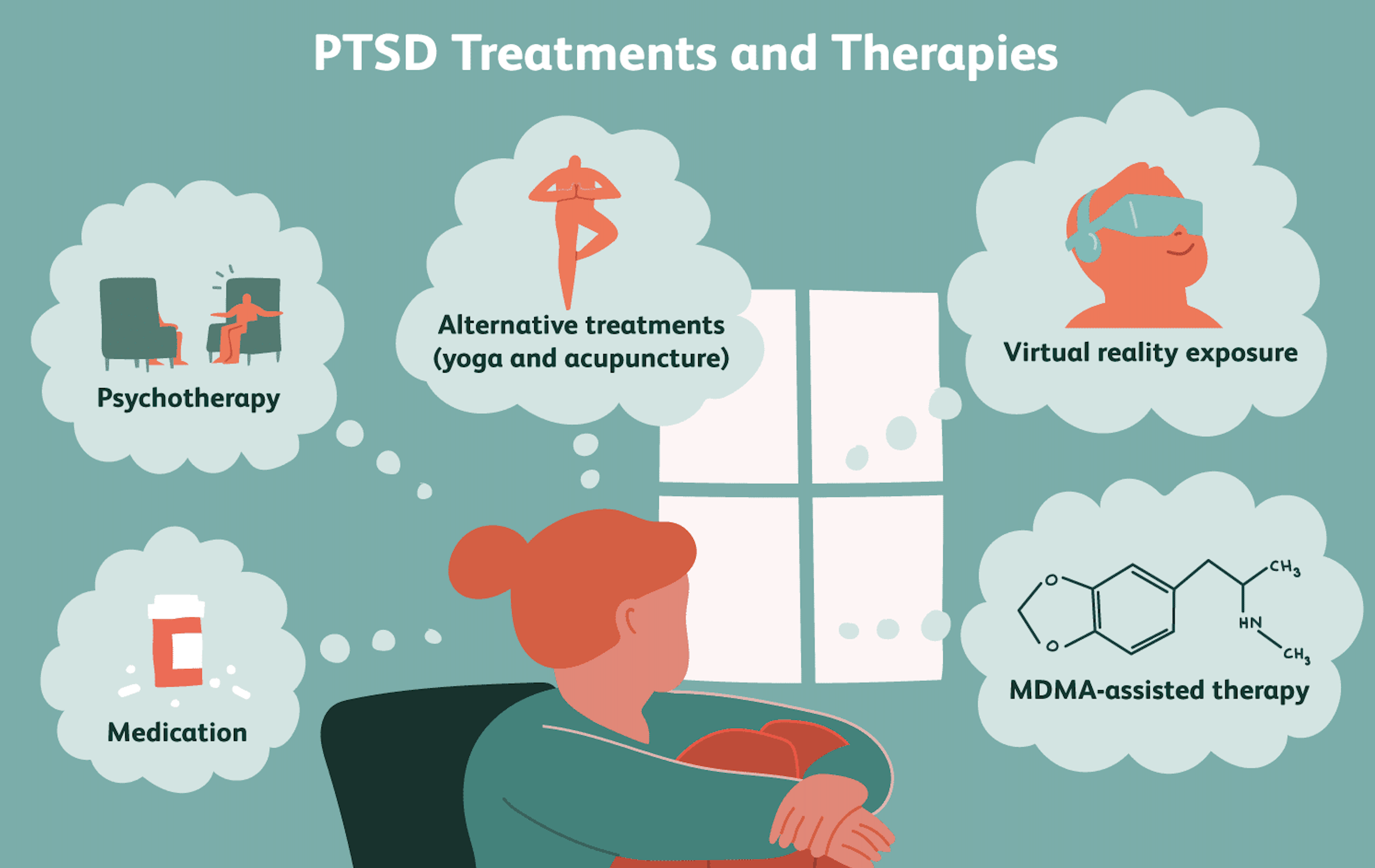
Treating PTSD and dissociation demands a comprehensive and tailored approach, ensuring that each individual's unique needs are met. Psychotherapy often serves as the cornerstone of treatment, with methods such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) demonstrating significant effectiveness in alleviating PTSD symptoms by helping patients process and integrate traumatic memories. For managing dissociation, therapies that emphasize grounding techniques and mindfulness prove beneficial, as they aid in reconnecting individuals with their present reality and enhancing their sense of self. The integration of medication can also be crucial, offering symptom relief and enabling individuals to engage more effectively in therapeutic processes. Support networks, whether familial, social, or community-based, provide an invaluable layer of reinforcement, fostering a sense of belonging and emotional safety. Ultimately, creating individualized treatment plans is vital, as it allows healthcare providers to address the intricate interplay of PTSD and dissociative symptoms, paving the way for holistic healing and recovery..
Complex PTSD: A Need For Specialized Care
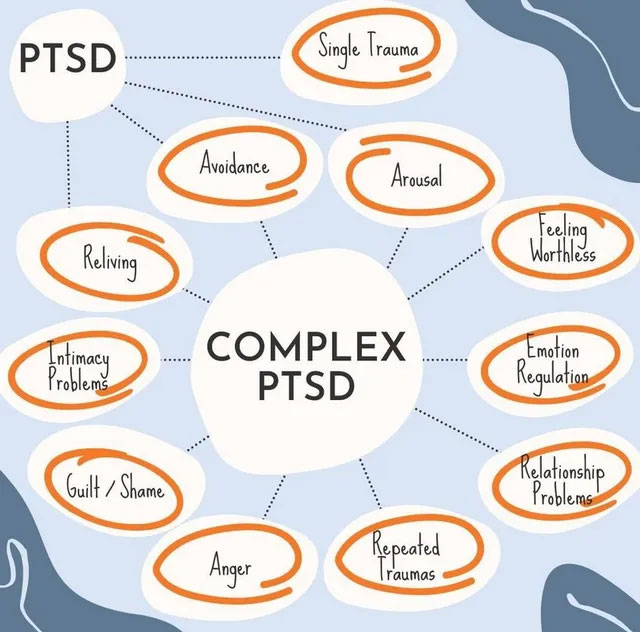
Unlike general PTSD, complex PTSD demands specialized therapeutic interventions that extend beyond standard trauma-focused therapy. This condition requires a multifaceted approach, targeting not just the distressing trauma memories but also the broader aspects of emotional regulation, interpersonal relationships, and self-perception. To effectively support individuals with complex PTSD, therapists often integrate components from Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), which is instrumental in managing the intense emotions and dissociative symptoms associated with this condition. DBT techniques, such as mindfulness, distress tolerance, emotional regulation, and interpersonal effectiveness, are crucial, as they empower individuals to navigate their inner turmoil and improve relational dynamics. By fostering greater awareness and acceptance through mindfulness practices, clients gain valuable tools to remain grounded, lessen emotional reactivity, and enhance their overall quality of life amidst the challenges posed by complex PTSD..
The Role Of Trauma-Informed Care
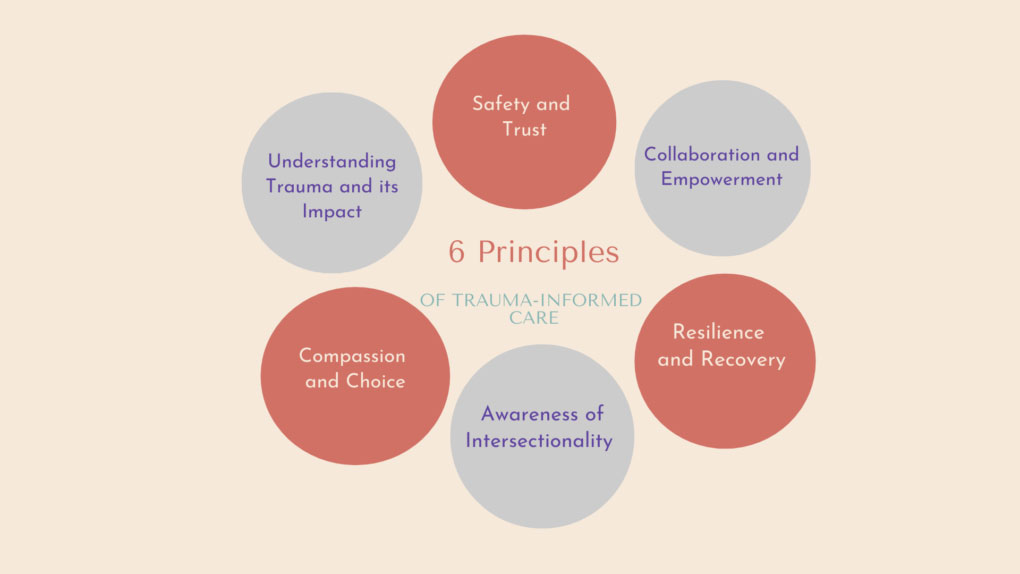
Trauma-informed care is becoming increasingly essential in mental health settings, as it not only acknowledges the widespread impact of trauma but also addresses its profound influence on mental health disorders such as PTSD and dissociation. This compassionate approach centers on creating environments where individuals feel safe, empowered, and trusted—key elements that facilitate the healing process. By involving clients in their treatment plans, trauma-informed care fosters a sense of agency and active participation, which are crucial for individuals who have experienced trauma. This collaborative process not only helps to rebuild trust and empowerment but also enhances the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. By prioritizing the individual's needs and experiences, practitioners of trauma-informed care are better equipped to support long-term recovery and resilience, ultimately contributing to a more holistic and empathetic approach to mental health treatment..
Living With PTSD And Dissociation
Recovery from PTSD and dissociation requires a multifaceted approach that embraces both professional guidance and personal resilience. Establishing a strong support network is crucial, whether it comes from family, friends, or support groups, as it provides a foundation of understanding and empathy. Engaging in self-care practices, such as mindfulness, exercise, and healthy eating, can help ground individuals and foster a sense of control over their lives. Consistency in treatment, whether it be therapy, medication, or alternative treatments, plays a pivotal role in managing symptoms effectively over time. By encouraging open conversations about mental health and actively working to reduce stigma, society can create a more inclusive environment where individuals feel empowered to seek the help they need without fear of judgment. In this nurturing space, those living with PTSD and dissociation can find hope and motivation to embrace their path toward healing..
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between PTSD and dissociation underscores the importance of a holistic approach to treatment and recovery. By prioritizing both trauma healing and the management of dissociative symptoms, individuals are empowered to achieve a more comprehensive and sustainable path to well-being. Ongoing research plays a pivotal role in uncovering new insights and refining therapeutic methods, while heightened awareness ensures that those affected receive the understanding and support they need. As the field advances, leveraging these developments will be key to fostering resilience and enabling individuals to thrive beyond their traumatic experiences.


